Does Italy Have a Death Penalty Currently in 2025?
Does Italy have a death penalty in 2025? This article explains Italy’s legal status, history, and cu...
Understanding the ideas of fusion of powers and separation of powers is absolutely key to seeing how governments divvy up authority.
Governments set up their power like a careful game of Jenga—making sure no single piece piles up high enough to topple the whole system into tyranny or inefficiency. By spreading out responsibilities and authority among various branches, political systems try to create a sort of chessboard of checks and balances. This separation acts as a protective shield for democratic values, helps curb any sneaky abuses.
Fusion of powers is a setup where the executive and legislative branches don’t just stand side by side—they roll up their sleeves and work hand in hand often sharing members and collaborating closely in the messy yet fascinating art of lawmaking and governance.
This system typically shows up in parliamentary democracies like the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia. The Prime Minister and cabinet members often wear two hats and serve as part of the legislature too which gives them a direct hand in shaping lawmaking.
Getting a grip on the separation of powers might seem like a dry topic at first glance, but stick with me—there's more to it than just legal jargon. It is essentially the backbone that keeps the government from turning into a chaotic free-for-all. By dividing responsibilities among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, each has its own turf to cover, preventing any one group from hogging all the power. It’s like a well-choreographed dance where everyone knows their steps, though sometimes those moves get a bit tangled in real life. Still, this balance is what keeps the democracy humming along smoothly, even when tensions rise and people start raising their voices. So, let’s dive in and see how this clever setup shapes how laws are made, enforced, and interpreted.
Separation of powers breaks down government authority into three branches: legislative, executive and judicial.
In the United States, Congress writes the laws. The President carries them out and the courts interpret what those laws actually mean.
| Category | Fusion of Powers | Separation of Powers |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Executive and legislature overlap or combine, often working hand in hand | Executive, legislature, and judiciary are kept distinct, each playing their own tune |
| Branch Relationship | Executive members often sit in the legislature, blurring lines just a bit | Branches operate independently, like well-trained soloists in an orchestra |
| Governance Style | Parliamentary system that leans heavily on party majorities | Presidential or mixed systems where branches keep a respectful distance, clearly defined |
| Examples | United Kingdom, Canada, Australia - places where teamwork is the name of the game | United States, France (semi-presidential model) - where checks and balances steal the show |
| Advantages | Faster decision-making, with a government that’s usually on the same page | Keeps tyranny at bay and flexes strong checks and balances to keep everyone honest |
| Disadvantages | Danger that the executive might run the show too much, weakening separation | Can get bogged down in gridlock, making progress a bit slower and more frustrating |
Fusion of powers often grabs attention for its knack for efficiency and its role in fostering political unity. It usually smooths the path to forming stable governments and getting policies off the ground quickly—especially in multiparty systems or situations where holding onto parliamentary support feels like a delicate juggling act.
The fusion of powers has its perks but often comes under fire because it can tip the scales, weakening the key checks and balances by funneling power into the hands of a dominant party or an executive-led coalition. This setup tends to chip away at legislative independence and hands the executive way too much control.
"When branches get too cozy, oversight can easily slip through the cracks — sometimes the very watchdogs find themselves unintentionally turning a blind eye to their own work, leaving things unchecked before anyone even notices."
Separation of powers is democracy’s watchdog that makes sure no single branch hogs all the power. It nudges each part to stay accountable and throws a wrench in any autocratic plans. It keeps the rule of law front and center by spreading government authority among independent bodies.
The fusion of powers is pretty much on full display in the United Kingdom since the Prime Minister and cabinet members also happen to be members of Parliament. This mix-and-match arrangement helps them stay in the good graces of the legislature, effortlessly blend policy-making with actually getting things done.
The United States keeps its powers neatly divided almost like a well-organized play where everyone knows their role. The President takes charge of the executive branch and runs things separately from Congress. The Supreme Court gets the final say on judicial matters. Each branch operates on its own turf with dedicated staff.
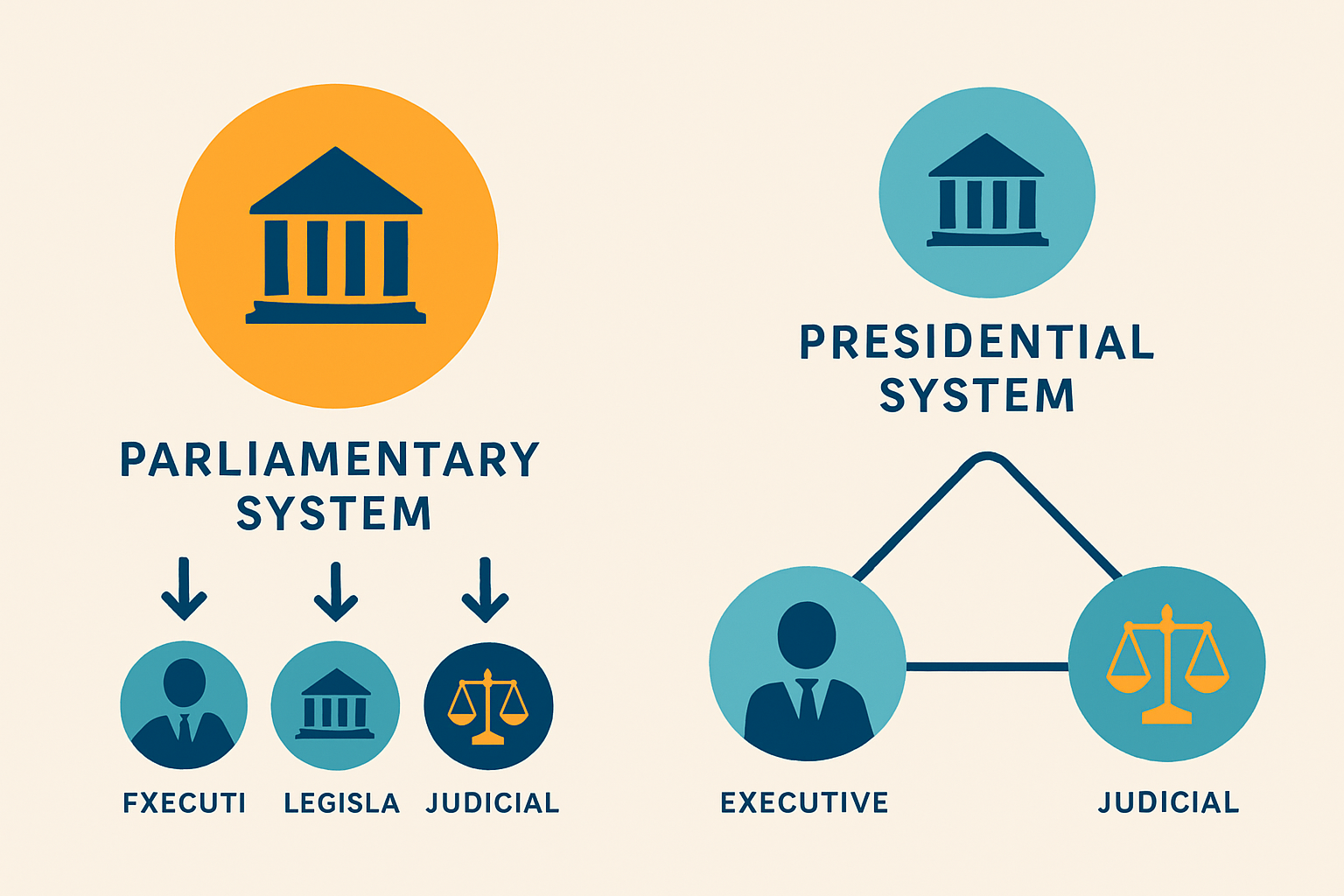
Diagram illustrating the structural and functional differences between fusion of powers and separation of powers.
These varied systems highlight the age-old tug-of-war between political stability and the need to act swiftly, versus safeguarding democratic protections and ensuring independent oversight.
Fusion of powers often gets a bad rap as if it means there’s no separation at all or that it inevitably leads to undemocratic rule. But if you dig a little deeper you’ll find that fusion systems usually maintain clear institutional boundaries and in their own quirky way can actually embody democratic values.
Understanding why the fusion of powers differs from the separation of powers sheds light on how each approach wrestles with the tricky business of governing. Both models come with their own perks and pitfalls and often align with different political traditions, cultures and priorities.
26 posts written
With experience in neuroscience journalism, Vesper makes cutting-edge brain research accessible to general audiences through clear explanations and compelling case studies.
Read Articles
Does Italy have a death penalty in 2025? This article explains Italy’s legal status, history, and cu...

Curious if Colombia grants birthright citizenship? This guide breaks down the country’s legal framew...

Wondering if Belize City is worth visiting? Explore its rich history, vibrant culture, stunning natu...

Explore the top travel adventure books that ignite the passion to wander, offering stories filled wi...
